“Software development” is an umbrella term for filling gaps within a company using technology that can automate operation and execution. Maybe you knew this and if you did then it wouldn’t be a surprise to learn that the development of this technology is quite complex. This may be the reason that more than half of tech executives outsource development projects. Let’s question why someone would do that, especially if they are experts within their business. Well, there is a plethora of possible reasons but let’s focus on 3:
1. Their internal team has too much on their plate.
2. The problem is too complex and they need a third party to help.
3. It is more efficient budget-wise to outsource development than to have a team on salary.
When it comes to a software company, there will be teams of developers with custom approaches to various situations. A software company's most basic yet important function is developing, designing, and maintaining software applications that help businesses perform. When a software company is tasked with a problem to solve, they face a series of considerations. These considerations are along the lines of the following questions:
What is the issue with the current application?
What will the timeline be to develop a new one?
What needs to be included?
What testing should be done?
When the team finalizes the action plan, the next step is planning for contingencies in the development process and how the team can be most efficient. There are numerous methodologies when it comes to the development process. This is because of how complex and broad the issues brought to software companies can be. With that being said, they must have an answer to even the most complex issues. Here are some of the main methods used to find those answers:
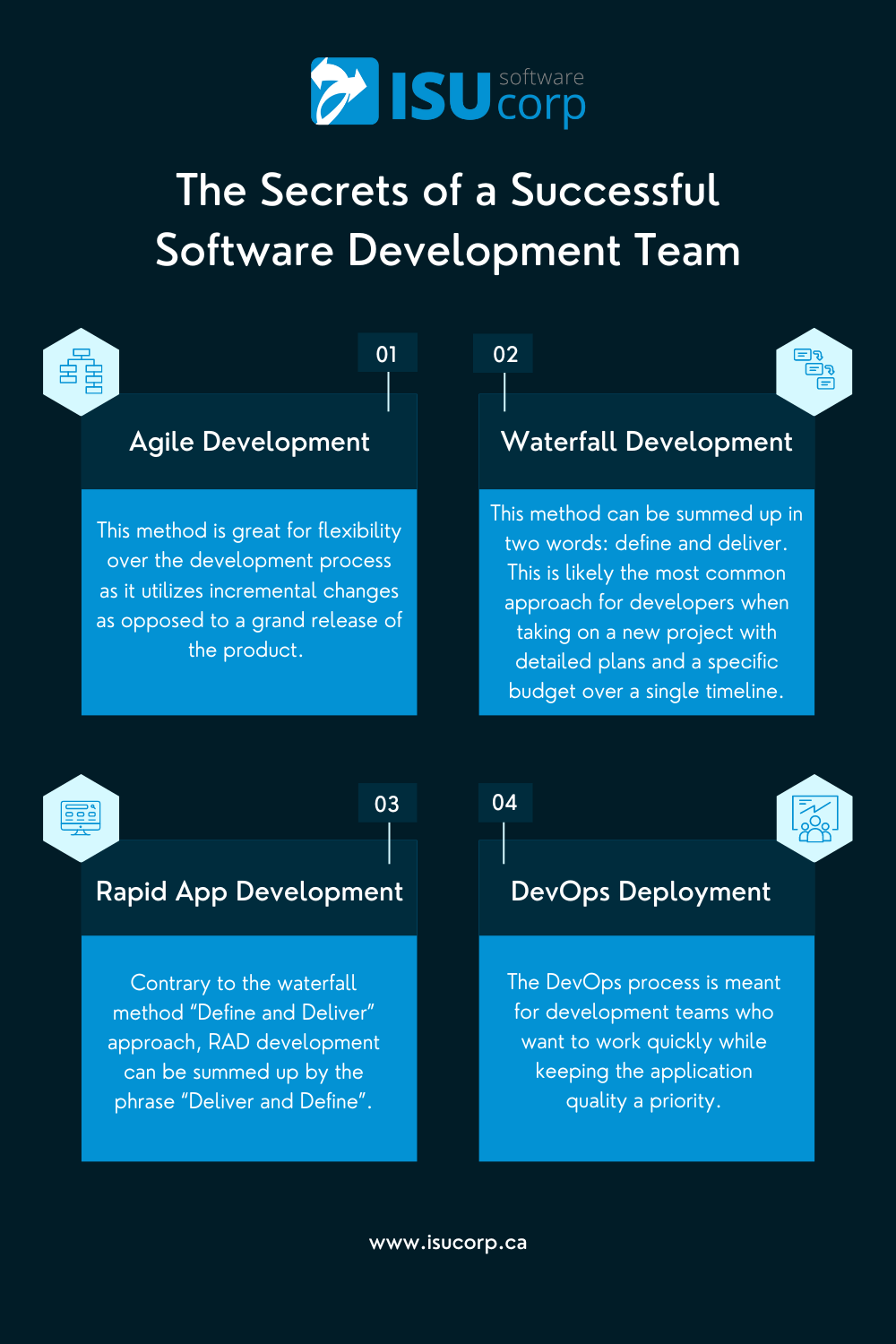
DevOps Deployment
The DevOps process is meant for development teams who want to work quickly while keeping the application quality a priority. Software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) are the two ends of building an application. These two sides can be better defined as developing the system and then continuing to improve on it.
With DevOps, these separate components are combined into one, meaning developers will construct an application while also focusing on feedback time, automating processes, and transparent data. This is to eliminate issues arising after the product has been implemented in the client's system. This approach is best suited for companies whose software issues don’t hurt operations significantly and only need occasional upgrades.
Waterfall Development
This method can be summed up in two words: define and deliver. This is likely the most common approach for developers when taking on a new project with detailed plans and a specific budget over a single timeline. The waterfall method follows a stage-by-stage plan in this order: Requirements, Design, Implementation, Verification, and Maintenance.
Each of these stages will have components that are subjective to the client and the needs of their industry. The steps need to be taken with caution, thorough planning, and detailed documentation. What’s especially useful with this approach is that it isolates each step of the development process. The team must ensure the quality of tasks completed before moving on as they won’t be able to go back and make changes without a price and impact the deadline.
Agile Development
This method is great for flexibility over the development process as it utilizes incremental changes as opposed to a grand release of the product. This is beneficial for projects that require continuous changes to the product (either influenced by the company or consumer) as it is continuously under the scope of the team. The timeline of one increment could last anywhere from a week to a month. During each period, developers will work to construct pieces of code or a function that they will add to the final product.
Agile development is easier on the development team as they won’t be rushing to finish something. Each step is consumable though it will require developers to be consistent and able to perform as a whole. A development team could be full of experts but have one member behind the rest. That one member will inhibit performance and cost time/money.
Rapid Application Development (RAD)
Contrary to the waterfall method “Define and Deliver” approach, RAD development can be summed up by the phrase “Deliver and Define”. A developer team using this method will develop a prototype of an application with no clearly defined guidelines. They will then present this to consumers and get their feedback to influence the changes made. The draw to this approach for software development companies is how quick the project turnaround is.
Developers are used to a fast-paced environment and this method is an efficient way to streamline the identification of what works for the consumer or what doesn’t. Once those areas are identified, the team can tweak the product to fit the targeted specifications. Now, this approach isn’t going to be used for large-scale projects. It best suits that of a small or medium-scale task for which timely completion is important.
How To Choose a Method
Choosing a software development method is completely dependent on the specifications of the project. The waterfall method can be used on projects of any size but it requires very strict guidelines compared to the others. The waterfall method is the only one that cannot make changes to its requirements and does not depend on user feedback. Now, small or medium projects are likely to utilize Agile or Rad which are both a bit more flexible with the guidelines but the timeline of completion is different. DevOps is used for bigger projects and has guidelines that will vary more than other methodologies.
This should paint a picture of the kind of subjectivity that software development projects depend on. In the end, a company that is outsourcing a project should identify a clear goal of what they want to accomplish with the product. Have this goal front-loaded when delegating your assignment either to your outsourced or in-house team.
Written By Ben Brown
We work with successful companies to increase their net profits using exceptional custom software solutions, contact us here to see how we can help your business grow!